LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) is a brand new method for tremendous tuning giant scale pre-trained
fashions. Such fashions are often skilled on common area information, in order to have
the utmost quantity of information. With the intention to receive higher ends in duties like chatting
or query answering, these fashions might be additional ‘fine-tuned’ or tailored on area
particular information.
It’s potential to fine-tune a mannequin simply by initializing the mannequin with the pre-trained
weights and additional coaching on the area particular information. With the rising measurement of
pre-trained fashions, a full ahead and backward cycle requires a considerable amount of computing
sources. Effective tuning by merely persevering with coaching additionally requires a full copy of all
parameters for every job/area that the mannequin is customized to.
LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Giant Language Fashions
proposes an answer for each issues by utilizing a low rank matrix decomposition.
It could possibly scale back the variety of trainable weights by 10,000 occasions and GPU reminiscence necessities
by 3 occasions.
Technique
The issue of fine-tuning a neural community might be expressed by discovering a (Delta Theta)
that minimizes (L(X, y; Theta_0 + DeltaTheta)) the place (L) is a loss perform, (X) and (y)
are the info and (Theta_0) the weights from a pre-trained mannequin.
We study the parameters (Delta Theta) with dimension (|Delta Theta|)
equals to (|Theta_0|). When (|Theta_0|) may be very giant, similar to in giant scale
pre-trained fashions, discovering (Delta Theta) turns into computationally difficult.
Additionally, for every job it is advisable to study a brand new (Delta Theta) parameter set, making
it much more difficult to deploy fine-tuned fashions when you have greater than a
few particular duties.
LoRA proposes utilizing an approximation (Delta Phi approx Delta Theta) with (|Delta Phi| << |Delta Theta|).
The commentary is that neural nets have many dense layers performing matrix multiplication,
and whereas they sometimes have full-rank throughout pre-training, when adapting to a particular job
the burden updates could have a low “intrinsic dimension”.
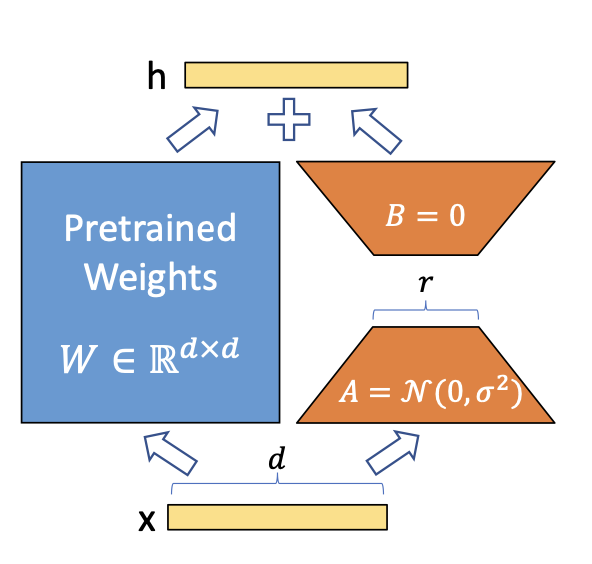
A easy matrix decomposition is utilized for every weight matrix replace (Delta theta in Delta Theta).
Contemplating (Delta theta_i in mathbb{R}^{d occasions ok}) the replace for the (i)th weight
within the community, LoRA approximates it with:
[Delta theta_i approx Delta phi_i = BA]
the place (B in mathbb{R}^{d occasions r}), (A in mathbb{R}^{r occasions d}) and the rank (r << min(d, ok)).
Thus as an alternative of studying (d occasions ok) parameters we now must study ((d + ok) occasions r) which is well
quite a bit smaller given the multiplicative side. In apply, (Delta theta_i) is scaled
by (frac{alpha}{r}) earlier than being added to (theta_i)which might be interpreted as a
‘studying price’ for the LoRA replace.
LoRA doesn’t enhance inference latency, as as soon as tremendous tuning is completed, you’ll be able to merely
replace the weights in (Theta) by including their respective (Delta theta approx Delta phi).
It additionally makes it easier to deploy a number of job particular fashions on prime of 1 giant mannequin,
as (|Delta Phi|) is far smaller than (|Delta Theta|).
Implementing in torch
Now that we’ve got an concept of how LoRA works, let’s implement it utilizing torch for a
minimal drawback. Our plan is the next:
- Simulate coaching information utilizing a easy (y = X theta) mannequin. (theta in mathbb{R}^{1001, 1000}).
- Prepare a full rank linear mannequin to estimate (theta) – this will probably be our ‘pre-trained’ mannequin.
- Simulate a distinct distribution by making use of a change in (theta).
- Prepare a low rank mannequin utilizing the pre=skilled weights.
Let’s begin by simulating the coaching information:
library(torch)
n <- 10000
d_in <- 1001
d_out <- 1000
thetas <- torch_randn(d_in, d_out)
X <- torch_randn(n, d_in)
y <- torch_matmul(X, thetas)We now outline our base mannequin:
mannequin <- nn_linear(d_in, d_out, bias = FALSE)We additionally outline a perform for coaching a mannequin, which we’re additionally reusing later.
The perform does the usual traning loop in torch utilizing the Adam optimizer.
The mannequin weights are up to date in-place.
prepare <- perform(mannequin, X, y, batch_size = 128, epochs = 100) {
decide <- optim_adam(mannequin$parameters)
for (epoch in 1:epochs) {
for(i in seq_len(n/batch_size)) {
idx <- pattern.int(n, measurement = batch_size)
loss <- nnf_mse_loss(mannequin(X[idx,]), y[idx])
with_no_grad({
decide$zero_grad()
loss$backward()
decide$step()
})
}
if (epoch %% 10 == 0) {
with_no_grad({
loss <- nnf_mse_loss(mannequin(X), y)
})
cat("[", epoch, "] Loss:", loss$merchandise(), "n")
}
}
}The mannequin is then skilled:
prepare(mannequin, X, y)
#> [ 10 ] Loss: 577.075
#> [ 20 ] Loss: 312.2
#> [ 30 ] Loss: 155.055
#> [ 40 ] Loss: 68.49202
#> [ 50 ] Loss: 25.68243
#> [ 60 ] Loss: 7.620944
#> [ 70 ] Loss: 1.607114
#> [ 80 ] Loss: 0.2077137
#> [ 90 ] Loss: 0.01392935
#> [ 100 ] Loss: 0.0004785107OK, so now we’ve got our pre-trained base mannequin. Let’s suppose that we’ve got information from
a slighly totally different distribution that we simulate utilizing:
thetas2 <- thetas + 1
X2 <- torch_randn(n, d_in)
y2 <- torch_matmul(X2, thetas2)If we apply out base mannequin to this distribution, we don’t get a great efficiency:
nnf_mse_loss(mannequin(X2), y2)
#> torch_tensor
#> 992.673
#> [ CPUFloatType{} ][ grad_fn = ] We now fine-tune our preliminary mannequin. The distribution of the brand new information is simply slighly
totally different from the preliminary one. It’s only a rotation of the info factors, by including 1
to all thetas. Which means that the burden updates are usually not anticipated to be advanced, and
we shouldn’t want a full-rank replace to be able to get good outcomes.
Let’s outline a brand new torch module that implements the LoRA logic:
lora_nn_linear <- nn_module(
initialize = perform(linear, r = 16, alpha = 1) {
self$linear <- linear
# parameters from the unique linear module are 'freezed', so they aren't
# tracked by autograd. They're thought-about simply constants.
purrr::stroll(self$linear$parameters, (x) x$requires_grad_(FALSE))
# the low rank parameters that will probably be skilled
self$A <- nn_parameter(torch_randn(linear$in_features, r))
self$B <- nn_parameter(torch_zeros(r, linear$out_feature))
# the scaling fixed
self$scaling <- alpha / r
},
ahead = perform(x) {
# the modified ahead, that simply provides the outcome from the bottom mannequin
# and ABx.
self$linear(x) + torch_matmul(x, torch_matmul(self$A, self$B)*self$scaling)
}
)We now initialize the LoRA mannequin. We’ll use (r = 1)which means that A and B will probably be simply
vectors. The bottom mannequin has 1001×1000 trainable parameters. The LoRA mannequin that we’re
are going to tremendous tune has simply (1001 + 1000) which makes it 1/500 of the bottom mannequin
parameters.
lora <- lora_nn_linear(mannequin, r = 1)Now let’s prepare the lora mannequin on the brand new distribution:
prepare(lora, X2, Y2)
#> [ 10 ] Loss: 798.6073
#> [ 20 ] Loss: 485.8804
#> [ 30 ] Loss: 257.3518
#> [ 40 ] Loss: 118.4895
#> [ 50 ] Loss: 46.34769
#> [ 60 ] Loss: 14.46207
#> [ 70 ] Loss: 3.185689
#> [ 80 ] Loss: 0.4264134
#> [ 90 ] Loss: 0.02732975
#> [ 100 ] Loss: 0.001300132 If we take a look at (Delta theta) we’ll see a matrix filled with 1s, the precise transformation
that we utilized to the weights:
delta_theta <- torch_matmul(lora$A, lora$B)*lora$scaling
delta_theta[1:5, 1:5]
#> torch_tensor
#> 1.0002 1.0001 1.0001 1.0001 1.0001
#> 1.0011 1.0010 1.0011 1.0011 1.0011
#> 0.9999 0.9999 0.9999 0.9999 0.9999
#> 1.0015 1.0014 1.0014 1.0014 1.0014
#> 1.0008 1.0008 1.0008 1.0008 1.0008
#> [ CPUFloatType{5,5} ][ grad_fn = ] To keep away from the extra inference latency of the separate computation of the deltas,
we might modify the unique mannequin by including the estimated deltas to its parameters.
We use the add_ technique to change the burden in-place.
with_no_grad({
mannequin$weight$add_(delta_theta$t())
})Now, making use of the bottom mannequin to information from the brand new distribution yields good efficiency,
so we are able to say the mannequin is customized for the brand new job.
nnf_mse_loss(mannequin(X2), y2)
#> torch_tensor
#> 0.00130013
#> [ CPUFloatType{} ]Concluding
Now that we discovered how LoRA works for this straightforward instance we are able to suppose the way it might
work on giant pre-trained fashions.
Seems that Transformers fashions are largely intelligent group of those matrix
multiplications, and making use of LoRA solely to those layers is sufficient for decreasing the
tremendous tuning price by a big quantity whereas nonetheless getting good efficiency. You possibly can see
the experiments within the LoRA paper.
In fact, the thought of LoRA is straightforward sufficient that it may be utilized not solely to
linear layers. You possibly can apply it to convolutions, embedding layers and really some other layer.
Picture by Hu et al on the LoRA paper